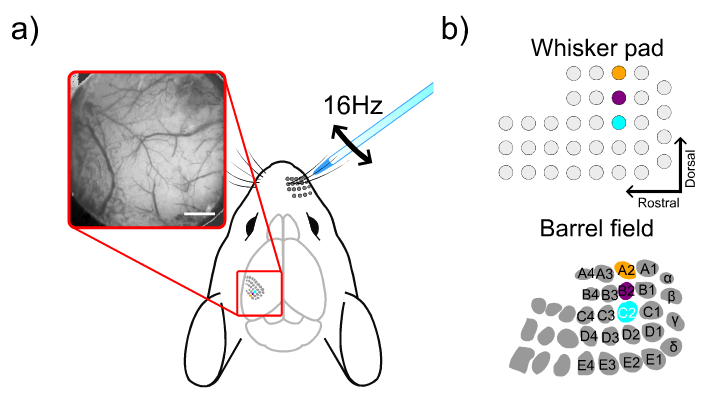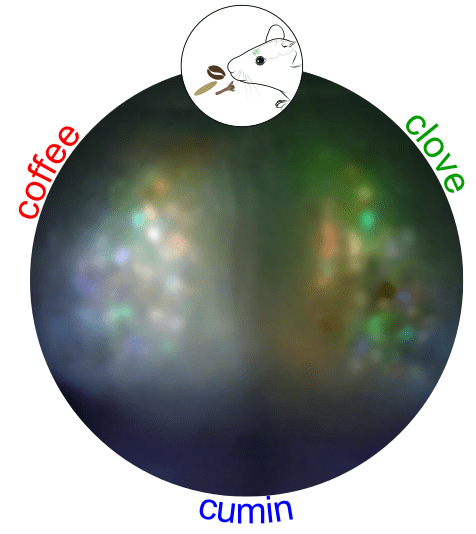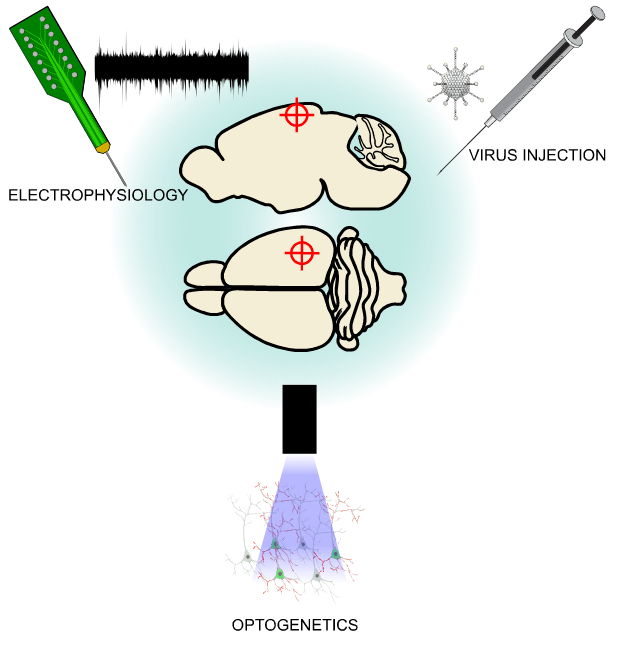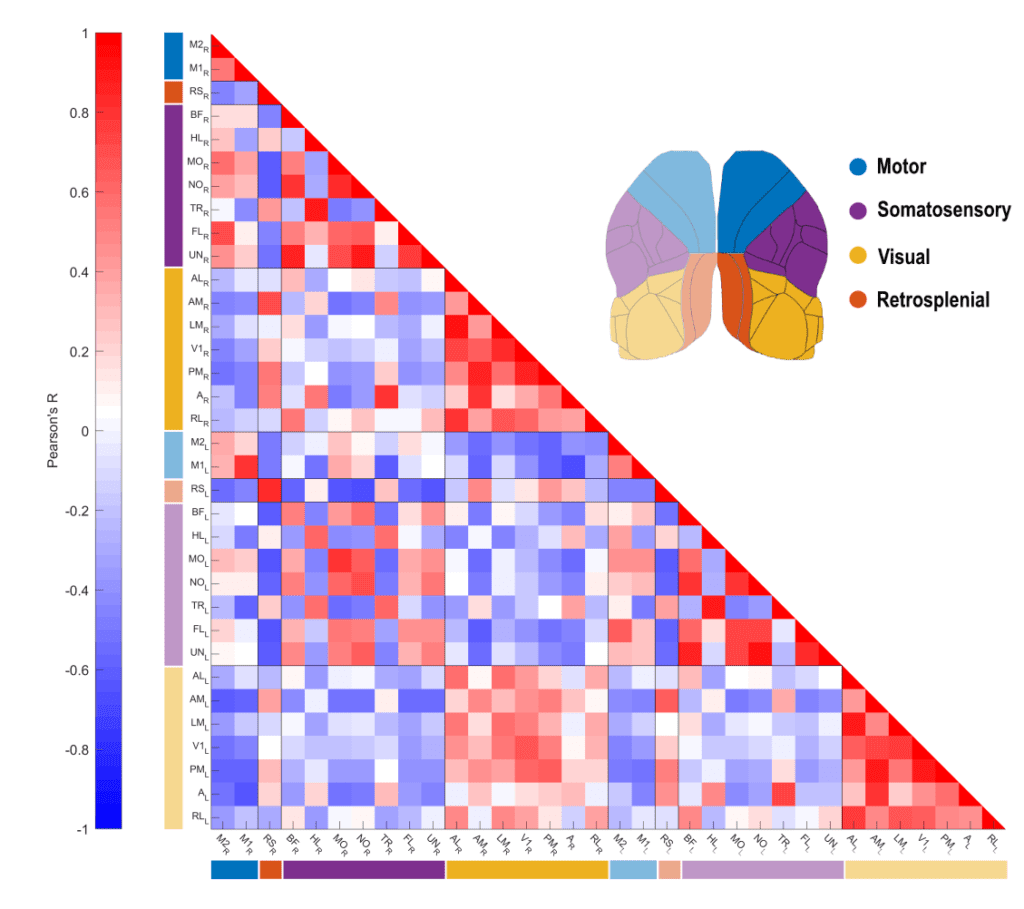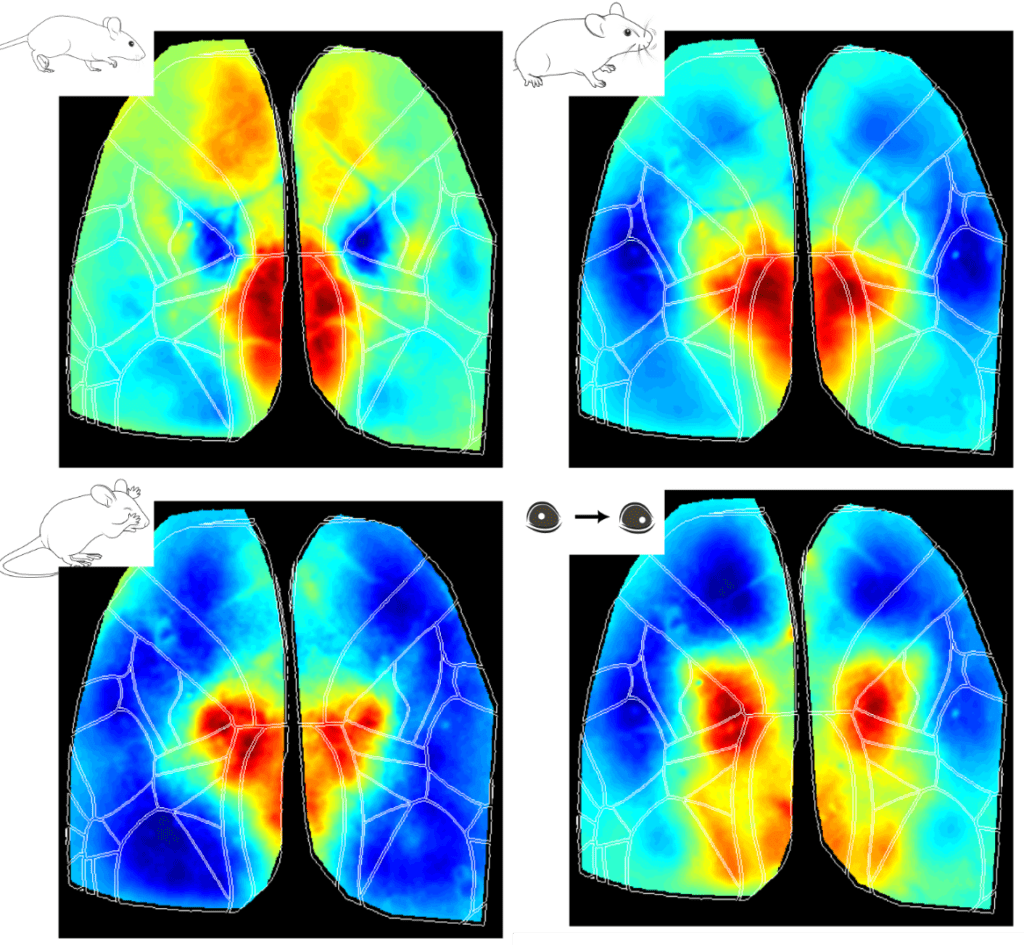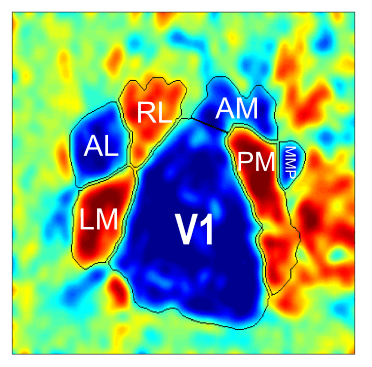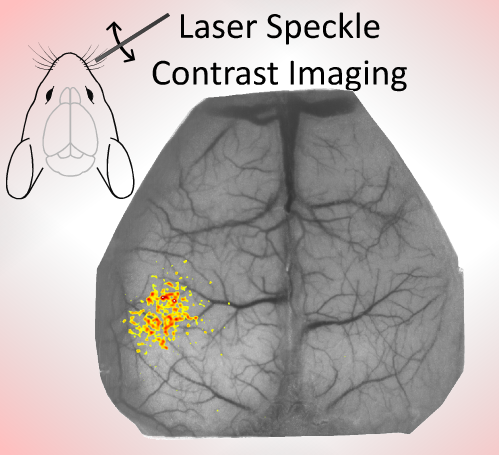
Exploring Cerebrovascular Dynamics with Widefield Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging
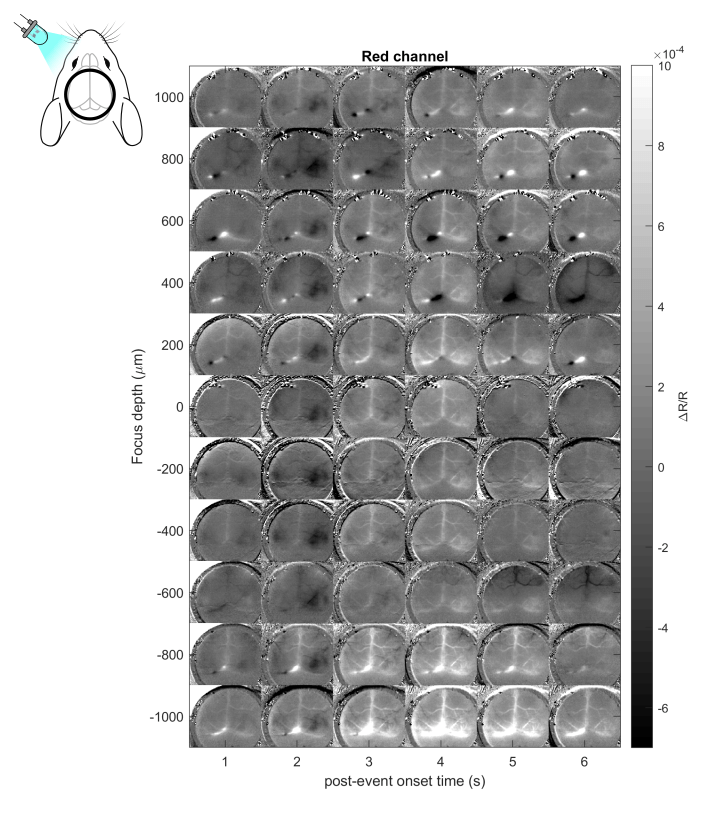
In this blog, we will explore another imaging technique that uses a completely different approach to reveal the vascular structure and blood flow of the brain tissue: laser speckle contrast imaging.
Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging (LSCI) is an imaging technique that enables the detection of particle flow (e.g. red blood cells) in a given medium (e.g. the brain). This technique is based on the interference of such moving particles on the speckle pattern detected by a camera.
The speckle pattern arises from the interaction of a coherent light source (i.e. laser) with the illuminated tissue. The reflected laser light captured by the camera’s sensor has traveled different paths inside the tissue, and the constructive and destructive sum of the light rays creates the random pattern in the image known as the speckle pattern.